Wrap definition encompasses a diverse range of meanings, from its literal interpretation as a protective covering to its metaphorical and idiomatic usage. In various contexts, wraps serve practical, aesthetic, and cultural purposes, shaping our interactions with the world around us.
From food packaging to clothing design, gift-giving to industrial applications, wraps play a multifaceted role in our daily lives, offering protection, preservation, and a touch of elegance.
Definition of Wrap: Wrap Definition

In its literal sense, “wrap” refers to the act of enveloping something by folding or covering it with a material. It implies a secure and protective enclosure.
Metaphorically, “wrap” can signify various concepts:
- To cover or conceal: “She wrapped her head in a scarf to shield herself from the cold.”
- To enclose or surround: “The fog wrapped the city in an eerie embrace.”
- To envelop in emotions or thoughts: “He was wrapped in a blanket of nostalgia.”
In idiomatic expressions, “wrap” can mean:
- To complete or finish: “Let’s wrap this up and move on.”
- To summarize or condense: “Can you give me a quick wrap of the main points?”
- To deceive or trick: “He wrapped me around his finger with his smooth talk.”
Types of Wraps
Wraps come in various categories, each serving specific purposes:
Food Wraps
Food wraps are designed to preserve and protect food items. They include:
- Plastic wrap:Transparent and stretchable, ideal for sealing containers or wrapping sandwiches.
- Aluminum foil:Reflective and opaque, suitable for roasting and baking.
- Wax paper:Grease-resistant, commonly used for wrapping sandwiches or lining baking sheets.
Clothing Wraps
Clothing wraps provide warmth, protection, or style:
- Scarves:Worn around the neck for warmth and accessorizing.
- Shawls:Large, rectangular wraps used for warmth and elegance.
- Turbans:Head coverings that can serve cultural, religious, or fashion purposes.
Gift Wraps
Gift wraps enhance the presentation of gifts:
- Paper:Decorative and colorful, available in various patterns and designs.
- Fabric:Luxurious and reusable, often used for special occasions.
- Ribbons and bows:Add a touch of elegance and festivity to gifts.
Materials and Techniques
Wraps are made from various materials, each with unique properties:
Materials
- Paper:Lightweight, flexible, and biodegradable.
- Fabric:Durable, breathable, and can be reused.
- Plastic:Waterproof, transparent, and stretchable.
- Metal:Strong, opaque, and often used for food packaging.
Techniques
Different wrapping techniques are employed depending on the purpose:
- Rolling:Wrapping an item by rolling it up, often used for food wraps and gift wrapping.
- Folding:Creating neat and precise folds, common in origami and gift wrapping.
- Bundling:Securing multiple items together, typically used for clothing wraps and gift baskets.
Purpose and Function
Wraps serve various purposes:
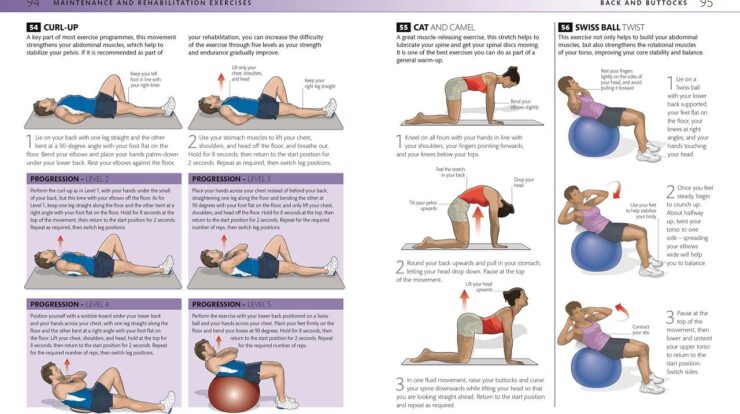
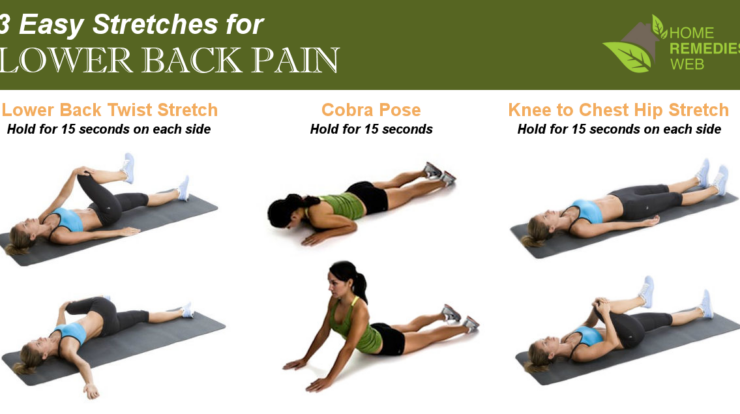
Protection
Wraps protect items from external factors such as moisture, dust, and damage.
Preservation
Food wraps help preserve freshness and extend the shelf life of food.
Aesthetics
Wraps enhance the visual appeal of gifts, products, and environments.
Convenience
Wraps make it easy to store, transport, and handle items.
Communication
Gift wraps convey messages of celebration, appreciation, or affection.
Cultural Significance, Wrap definition
Wrapping rituals and customs hold cultural significance:
- Japanese furoshiki:Traditional fabric wraps used for various purposes, including gift-giving and carrying belongings.
- Indian dupatta:A versatile wrap worn by women, serving both practical and decorative functions.
- Scottish tartan:Distinctive plaid fabric used in clothing and wraps, representing clan identity and heritage.
Examples of Wrap Applications
Wraps are used in numerous industries and situations:
- Food packaging:Protecting and preserving food items.
- Clothing design:Enhancing warmth, style, and comfort.
- Gift-giving:Making gifts visually appealing and meaningful.
- Interior design:Adding texture, color, and warmth to spaces.
- Medical and healthcare:Sterilizing and protecting medical instruments and supplies.
Wrap Design and Aesthetics
Wrap design involves considering aesthetic factors:
- Color and pattern:Choosing colors and patterns that complement the wrapped item and intended purpose.
- Texture:Utilizing materials with different textures to create visual interest and tactile appeal.
- Shape and form:Creating wraps with unique shapes and forms to enhance the overall presentation.
Innovations in Wrapping
Wrapping technology and materials continue to evolve:
- Biodegradable wraps:Eco-friendly alternatives to plastic wraps, made from plant-based materials.
- Smart wraps:Incorporating sensors or indicators to monitor the condition of wrapped items.
- Reusable wraps:Durable and washable wraps designed to minimize waste.
Last Point
The art of wrapping has evolved over time, embracing new materials and innovative techniques. As we delve deeper into the world of wraps, we uncover their cultural significance, symbolic meanings, and the latest trends shaping their design and functionality.
Question Bank
What is the primary purpose of wrapping?
Protection, preservation, and aesthetics.
What are the different types of wraps?
Food wraps, clothing wraps, gift wraps, industrial wraps, etc.
What materials are commonly used for wrapping?
Paper, fabric, plastic, metal, etc.